The technology stack for startups you choose shapes how quickly you can turn ideas into a shipped product. A well-chosen startup technology stack, including a web development stack for startups, accelerates iteration and helps your team stay productive with a shared language. From cloud infrastructure for startups to frontend and backend decisions, these choices determine performance, reliability, and time to market. In this guide, we’ll explain how to choose tech stack for startups using a practical framework that balances speed, cost, and long-term viability. A thoughtful approach emphasizes a scalable tech stack for startups and maintainability so you build a foundation that can grow with your product.
Beyond the exact labels, startups benefit from a flexible software architecture and a practical engineering toolkit that keeps delivery fast. Think in terms of a modern tech ecosystem—managed services, well-defined API boundaries, and a cloud-first mindset that reduces on-premise complexity. This perspective aligns with the same goals described earlier: rapid iterations, predictable costs, and options to scale as user demand grows. Using alternative LSI-friendly terminology such as development toolkit for new ventures or IT landscape for early-stage companies helps teams stay focused on outcomes rather than flashy labels.
Technology stack for startups: How to choose a startup technology stack for scalable growth
Choosing the technology stack for a startup is a strategic decision with long-lasting impact. When evaluating the technology stack for startups, you should weigh speed to market, team capability, and long-term maintenance costs. Aligning the decision with the concept of a startup technology stack helps you stay outcome-focused rather than chasing the latest gadget. This is where how to choose tech stack for startups becomes practical: prioritize patterns and tools that reduce boilerplate, enable rapid iteration, and simplify onboarding for new engineers. The result is a foundation that supports MVP timelines while keeping options open for future growth. By tying technical choices to product goals and talent strategy, you improve your odds of delivering quickly without incurring unsustainable debt.
A practical framework anchors the process in reality. Start by defining product goals and constraints, then map roles and hiring velocity, followed by shortlisting options by layer: frontend, backend, data storage, and DevOps. This approach fosters a scalable tech stack for startups because it makes capacity planning explicit and creates a clear migration path. When evaluating candidates, select a web development stack for startups that offers fast development cycles, a healthy ecosystem, and enterprise-grade tooling. Finally, pilot a small feature to validate developer experience, performance, and operations, and plan for growth with data migration and backward-compatibility considerations. Also consider cloud infrastructure for startups to minimize operational overhead and accelerate deployment through managed services.
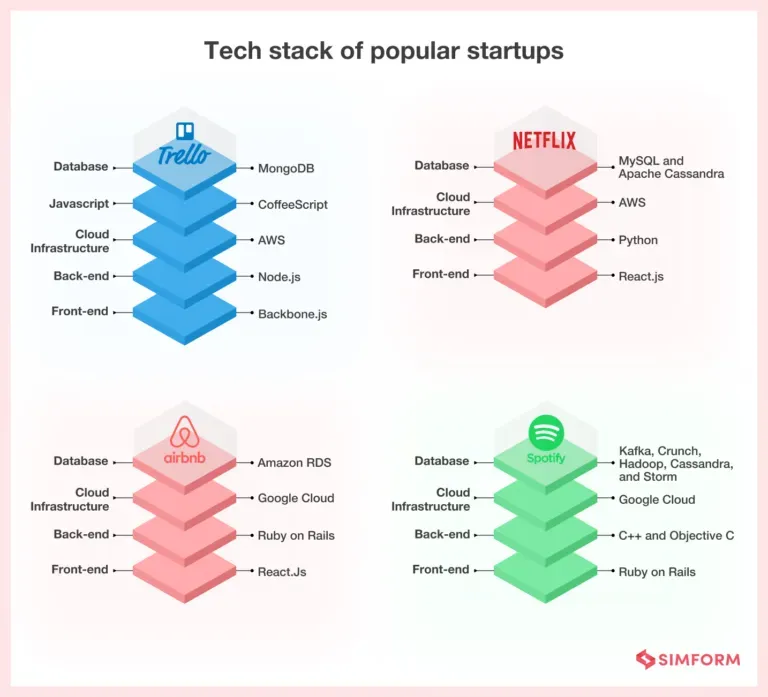
Cloud infrastructure and frontend/backend choices: building a scalable web development stack for startups
Frontend and backend choices are tightly connected and influence both user experience and operational reliability. For frontend, frameworks like React, Vue, and Angular offer different trade-offs, but what matters most is team proficiency, component ecosystems, and performance patterns. When you align this with a sound backend, you can craft a resilient web development stack for startups that supports REST or GraphQL APIs, authentication schemes, and graceful degradation under load. A modular approach—whether a well-structured monolith or an evolving microservices pattern—lets you ship quickly while keeping future refactoring manageable. Prioritize a clean developer experience, strong tooling, and accessible interfaces so onboarding is smooth and features ship reliably.
On the cloud side, cloud infrastructure for startups should emphasize managed services, observability, and security by design. Evaluate providers on global reach, service maturity, cost, and integration with your chosen stack. Build automated CI/CD pipelines, extensive monitoring, logging, and tracing from day one, and adopt security best practices like encryption, identity management, and regular audits. The goal is a scalable web development stack for startups that remains affordable as traffic grows, while providing predictable reliability, faster recovery from failures, and clear ownership of architectural decisions. By combining frontend/backend choices with a robust cloud strategy, you create a resilient product foundation that can evolve from MVP to scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to choose tech stack for startups to build a scalable tech stack for startups?
Follow a practical decision framework: define MVP goals, target platforms, and a rough budget; map your team skills and hiring velocity; shortlist options by layer (frontend, backend, data, DevOps); validate with a small pilot to measure build time, deployment speed, reliability, and error rates; plan for growth with a migration path and modular architecture. Favor patterns that accelerate delivery such as MERN style stacks for fast web MVPs or serverless and cloud native approaches, and design the stack to become a scalable tech stack for startups. Rely on managed services to reduce maintenance while balancing vendor lock in, and invest in security, testing, and observability from day one. The result is a startup technology stack that moves quickly, ships reliably, and scales as you grow.
What factors should you consider when selecting a web development stack for startups and cloud infrastructure for startups?
Key considerations include frontend choices (React, Vue, or Angular) with fast iteration, accessibility, and a solid component ecosystem; backend options (Node.js, Python, Go, Ruby, Java) based on team skills and performance needs; API design (REST or GraphQL) and the choice between a modular monolith or microservices. Develop a data strategy around relational vs NoSQL databases and caching, and plan for observability and security from the start. For cloud infrastructure for startups, evaluate providers like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for maturity and cost, and favor managed services such as databases, queues, and serverless compute to reduce operational overhead. Establish CI/CD pipelines, enforce security by design, and plan for scaling with a clear migration path. In a web development stack for startups, this approach helps balance speed, reliability, and long term viability while remaining adaptable as you scale.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| What is a startup tech stack? | Definition: the combination of software tools, frameworks, libraries, and infrastructure that powers your product from the client side to the server, data storage, and operations; chosen to balance speed, cost, flexibility, and risk; aligned with product goals, team strengths, and go-to-market plan. |
| Why it matters | Impact: it shapes speed to market, maintenance costs, talent attraction, and risk management; a well-chosen stack enables faster shipping and easier onboarding, while a poor choice can slow growth and increase debt. |
| Key criteria to evaluate | Speed to market; team proficiency and hiring velocity; scalability and performance; cost and total cost of ownership; maintainability and governance; security and compliance; ecosystem and long-term viability; observability and operations. |
| Practical decision framework | Define goals and constraints; map roles and skills; shortlist stack candidates by layer (frontend, backend, data, DevOps); validate with a small pilot; plan for growth and migrations. |
| Common stack patterns | MERN/MEAN-like for rapid web development; LAMP/LEMP for reliability; JAMstack for fast frontends; serverless and microservices for speed and cost efficiency; cloud-native with managed services to reduce maintenance. |
| Frontend considerations | Frameworks (React, Vue, Angular); state management and modular architecture; performance, accessibility, and responsive design. |
| Backend and APIs | Language/framework options (Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, Java); API design (REST vs GraphQL); monolith vs microservices; emphasis on scalability and developer experience. |
| Data strategy | Relational vs NoSQL; caching and performance; analytics and telemetry from day one. |
| Cloud infrastructure and DevOps | Cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud); CI/CD and automation; observability; security by design; prefer managed services to reduce maintenance. |
| Practical examples | Consumer web apps with MERN + serverless APIs; data-driven SaaS with robust relational DBs and data pipelines; enterprise-grade tools with strong security and compliance. |
| Risk minimization | Start small but think long-term; favor managed services; invest in testing and observability from day one; document architectural decisions; align tech with business milestones. |
| Implementation plan (timeline) | Week 1–2: define MVP goals; Week 2–6: build MVP with CI/CD and monitoring; Month 2–3: collect feedback and optimize; Month 4–6: scale prep, data strategy, and security focus. |
| Common pitfalls | Over-optimizing before validating product-market fit; chasing buzzword stacks without business rationale; underestimating developer onboarding; underinvesting in security, backups, and disaster recovery. |
Summary
technology stack for startups is a practical, iterative decision process that balances speed, cost, and long-term viability. This descriptive conclusion highlights how a thoughtful evaluation of frontend, backend, data, and infrastructure options, together with small pilots and growth planning, enables rapid delivery while staying adaptable. By emphasizing modular architecture, strong observability, and alignment with business milestones, teams can ship reliably, scale gracefully, and attract top talent. In short, the technology stack for startups should fit the team, support rapid iteration, and grow with the product, keeping the user at the center of every decision.