In recent years, there has been a concerning increase in heart attacks across the United States, as medical experts highlight a notable rise in cardiac deaths, particularly at home. Data illustrates that the years following the Covid-19 pandemic have seen a staggering escalation in heart-related fatalities, with some reports indicating a 17 percent spike in home deaths due to heart disease. While hospital admissions for heart attacks have dipped, the rise in home cardiac fatalities calls for urgent attention to heart health and the impact of care gaps. Covid-19’s influence on heart health cannot be overlooked, as it may contribute to complications like myocarditis and affect lifestyle choices that further predispose individuals to heart disease post-pandemic. It is essential to address these rising challenges in the context of heart attack increase, ensuring that effective preventive measures and timely interventions are prioritized to safeguard public health.
The alarming trend of rising heart attack incidents can also be viewed through the lens of increasing cardiovascular afflictions among the populace. Throughout the aftermath of the pandemic, many individuals face a heightened risk of cardiac-related fatalities, with statistics revealing a growing number of those succumbing to heart disease at home rather than in medical facilities. This shift has prompted an examination of the broader implications of healthcare access and disease management in the context of Covid-19’s lingering effects on health systems. Additionally, the gradual rise in cases of myocarditis following Covid-19 infections points to potential underlying issues that necessitate deeper investigation into long-term heart health consequences. By exploring these alternative facets of cardiac mortality, we can better understand the emerging landscape of heart disease and its urgent demands for comprehensive care interventions and public health strategies.
The Alarming Rise in Heart Attacks Post-Covid
In the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic, health professionals have reported an alarming rise in heart attacks across the United States. Researchers from Mass General Brigham have identified a significant increase in cardiac deaths, with a staggering 17 percent rise noted in the years following the onset of the pandemic. This sharp uptick in fatalities is particularly concerning because many of these heart-related deaths are occurring at home, suggesting that underlying issues are being overlooked in the healthcare response to heart disease.
As hospitals reported fewer heart attack cases, partially due to reduced hospital visits during the pandemic, the overall mortality rates from cardiovascular conditions actually rose when considering home fatalities. Dr. Jason H. Wasfy emphasized the hidden danger of these statistics, noting that individuals displaying heart disease symptoms are not receiving timely medical intervention, which is critical in preventing fatal outcomes. This troubling trend underscores the need to understand how Covid-19 is amplifying risks associated with heart diseases.
Impact of Covid-19 on Heart Health
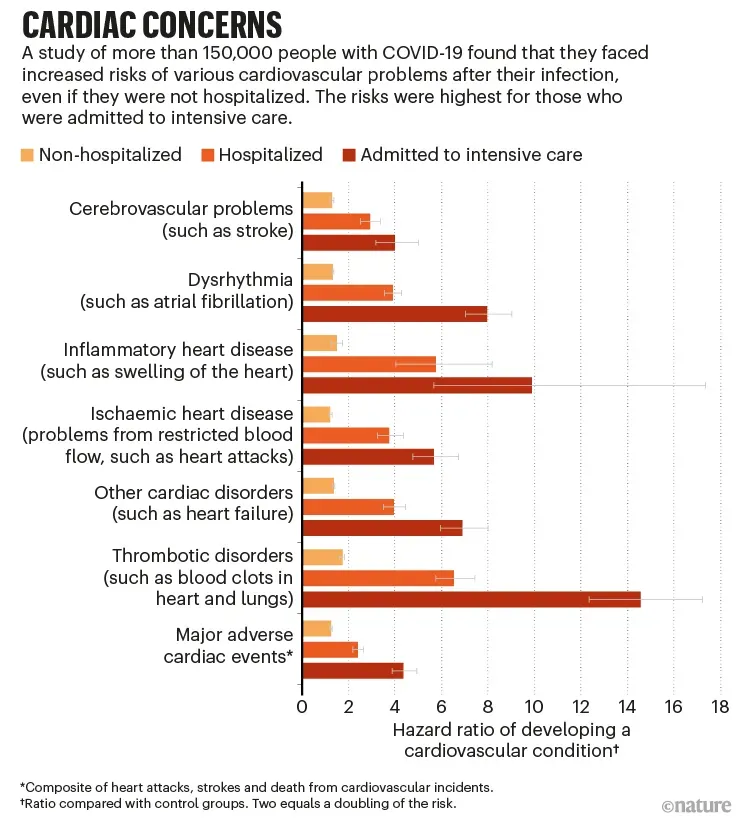
Covid-19’s impact on heart health has emerged as a serious concern among researchers and healthcare providers alike. Beyond the immediate effects of the virus, ample research suggests that individuals who have contracted Covid-19 may experience long-term cardiovascular issues, including myocarditis and pericarditis. These conditions, which involve inflammation of the heart, can severely affect individuals’ long-term health and recovery prospects. As such, understanding the broader implications of Covid-19 on heart health is essential for guiding patient care and preventive measures.
Moreover, researchers are investigating additional factors that may contribute to the deterioration of cardiac health in this period. Reports indicate that lifestyle changes during the pandemic—such as increased sedentary behavior, altered diets, and substance use—are exacerbating pre-existing heart conditions. As medical professionals work to address these challenges, they must remain vigilant to the resulting shifts in patient health outcomes, emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring of cardiac health post-pandemic.
Myocarditis and Other Heart Risks Following Covid-19
Myocarditis, or inflammation of the heart muscle, has gained attention as a potential complication associated with Covid-19 infections. This condition can lead to severe health issues, including heart failure or arrhythmias, posing a significant risk to recovery for previously healthy individuals. Medical studies note that while the incidence remains rare, the link to Covid-19, particularly in young adults and adolescents, raises alarms regarding vaccine-induced myocarditis which can echo similar immune responses triggered by the virus itself.
In light of these findings, healthcare systems need to enhance screening for cardiac-related symptoms among Covid-19 survivors. Prompt recognition and treatment of myocarditis and other cardiovascular complications are vital to ensure that those affected receive adequate care and improve their long-term outlook. As our understanding of these conditions evolves, the integration of cardiovascular care into post-Covid treatment plans will become increasingly important.
The Connection Between Home Cardiac Fatalities and Pandemic Isolation
The escalating number of cardiac deaths occurring at home post-pandemic highlights a disturbing trend rooted in pandemic-related isolation and healthcare accessibility issues. Many individuals, fearful of contracting the virus or overwhelmed by the sudden socio-economic changes, have opted to remain at home despite exhibiting troubling heart symptoms. This decision can have fatal consequences, as timely medical intervention is often crucial in managing acute heart conditions.
The risk of experiencing a heart attack without immediate medical help can mean the difference between life and death. Increased awareness and education about the signs of heart problems are necessary to encourage individuals to seek timely care, even amidst persistent pandemic concerns. Addressing the underlying fear that has deterred many from accessing healthcare facilities is vital to reversing the troubling trend of home cardiac fatalities.
Diet, Lifestyle Changes, and Heart Health Challenges
Diet and lifestyle changes during the Covid-19 pandemic have been substantial and, in many cases, detrimental to heart health. Increased reliance on convenience foods, limited physical activity, and higher stress levels have all contributed to the worsening of pre-existing heart conditions and an uptick in new cases of heart disease. Healthcare providers are noting an increased incidence of metabolic issues, including obesity, which is closely linked to cardiovascular risks.
To combat these emerging challenges, healthcare professionals are advocating for healthier lifestyle choices and increased physical activity among individuals, especially those with pre-existing heart disease. Encouraging balanced diets and regular exercise can bolster heart health and reduce the risks associated with Covid-19, thereby improving overall well-being during and following the pandemic.
Healthcare Access and Delayed Medical Attention
The Covid-19 pandemic has significantly affected individuals’ access to healthcare, contributing to alarming rates of untreated heart disease and an increase in cardiac deaths at home. Research indicates that many patients consider hospital visits risky and have chosen to forgo medical treatment for symptoms that may indicate serious heart conditions. This delay in seeking care can lead to more severe outcomes, including fatal heart attacks that could have been preventable with timely intervention.
To address this issue, healthcare systems must adapt to the needs of patients who are hesitant to come into medical facilities. Utilizing telehealth services and ensuring safe environments for in-person visits can reassure patients and encourage them to seek necessary cardiovascular care. Prioritizing heart health in post-pandemic recovery efforts will be critical to reversing these negative trends and improving overall cardiac health.
A Need for Increased Awareness of Heart Disease Symptoms
The increase in cardiac deaths at home following the pandemic emphasizes the crucial need for greater awareness around heart disease symptoms. Many individuals may not recognize the signs of a heart attack or other serious cardiac events, leading them to dismiss symptoms for too long and thereby risking their lives. Public health campaigns aimed at educating the populace about these symptoms are paramount in raising awareness and promoting proactive healthcare-seeking behavior.
Healthcare providers play a key role in this awareness campaign by disseminating information about the early warning signs of heart problems and encouraging regular health check-ups. By focusing on education, the healthcare community can help bridge the gap created by the pandemic and empower individuals to prioritize their heart health, which can ultimately save lives.
Reducing Marijuana Use to Protect Heart Health
Emerging studies have drawn a potentially concerning connection between regular marijuana use and heart health. Frequent consumption is correlated with impaired endothelial function, which significantly affects blood vessel dilation—a key factor in managing blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health. As the pandemic has shifted many individuals’ coping mechanisms, awareness around the possible risks of increased marijuana use is particularly pertinent.
Healthcare professionals are advocating for clear communication around the risks associated with substance use, particularly in relation to heart disease. By educating patients about the potential cardiovascular implications of marijuana use, medical practitioners can help individuals make informed choices concerning their health and mitigate risks associated with cardiac conditions.
The Future of Heart Health Care in a Post-Pandemic World
As we move further into a post-pandemic world, the landscape of heart health care must evolve to meet the new challenges that have emerged. Continued monitoring of changing patterns in cardiac health, combined with adapting healthcare delivery systems, will be essential in addressing the rising rates of heart attacks and cardiac deaths at home. This includes embracing telehealth solutions, improving patient education, and ensuring comprehensive outpatient support for individuals managing heart disease.
Furthermore, future research will be critical in uncovering the long-term impacts of Covid-19 on cardiovascular health, ideally leading to more enhanced protocols for early detection and treatment. As the healthcare community grapples with the aftermath of the pandemic, integrating lessons learned will be vital for protecting heart health and improving patient outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the reasons behind the increase in heart attack fatalities at home post Covid-19?
The increase in heart attack fatalities at home can be attributed to several factors, including delayed medical interventions and changes in health-seeking behaviors during and after the pandemic. Research indicates that many individuals have avoided seeking medical attention during the pandemic, leading to untreated heart disease and consequently more cardiac deaths at home.
How has the Covid-19 pandemic affected cardiac deaths in the United States?
The Covid-19 pandemic has resulted in a significant rise in cardiac deaths, with an increase of up to 17 percent in fatalities occurring at home. This rise highlights a concerning trend where individuals with heart disease may not be receiving timely medical care, as evidenced by a decline in heart attack hospitalizations during the post-pandemic period.
What is myocarditis, and how is it related to heart attack increases after Covid?
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart tissue, which can lead to serious conditions, including heart attacks. This condition has been linked to Covid-19 infection and, in rare cases, even to mRNA Covid vaccines, potentially contributing to the rise in cardiac deaths following the pandemic.
What impact has Covid-19 had on heart health and cardiac safety?
Covid-19 has been shown to contribute to heart damage and vascular complications, significantly impacting heart health. The increase in cardiac deaths post-pandemic suggests that many heart disease patients are not receiving the necessary precautions or medical care needed to manage their conditions effectively.
What lifestyle factors might be contributing to the increase in heart disease post-pandemic?
Post-pandemic lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise habits, may have contributed to the rise in heart disease. Studies indicate that factors such as increased stress, decreased physical activity, and dietary changes during and after the pandemic may elevate the risk of heart attacks.
How can marijuana use affect the risk of heart attacks?
Regular marijuana use has been associated with impaired endothelial function, potentially affecting blood vessel health and increasing the risk of heart attacks. This link underscores the importance of understanding lifestyle factors that may contribute to cardiac health post-pandemic.
What should individuals be aware of regarding heart health following the Covid-19 pandemic?
Individuals should remain vigilant about their heart health after the Covid-19 pandemic by seeking regular medical evaluations, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of the signs of heart disease or imminent cardiac events. Awareness and timely action are crucial in preventing increased heart attack fatalities.
Why is there a decline in heart attack hospitalizations despite the increase in cardiac deaths?
The decline in heart attack hospitalizations, despite the rise in cardiac deaths, suggests that many individuals are either delaying medical care or are not receiving adequate treatment due to altered healthcare-seeking behaviors during the pandemic.
What role do healthcare systems play in addressing the increase in heart attack fatalities?
Healthcare systems need to adapt to the changes in patient behavior and ensure that individuals with heart disease receive timely medical care. Increased awareness of cardiac health and the importance of seeking immediate care may help reduce the rise in cardiac deaths seen since the pandemic.
What further research is being conducted regarding heart health and pandemic effects?
Ongoing research is focused on understanding the comprehensive impacts of Covid-19 on heart health, including the long-term consequences of myocarditis and the overall rise in cardiac fatalities. This research aims to improve health strategies and interventions for heart disease management in the post-pandemic landscape.
| Key Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Concern Over Heart Attack Increase | Doctors report a significant rise in heart attacks and cardiac deaths, particularly at home. |
| Stats on Cardiac Deaths | Cardiac fatalities have surged by up to 17% in the years following the Covid-19 pandemic. |
| Hospital vs Home Deaths | Cardiac deaths at home increased, while in-hospital fatalities decreased, raising concerns. |
| Research Findings | A study on death certificates in Massachusetts revealed a 16% increase in cardiac deaths in 2020. |
| Impact of Covid-19 | Covid-19 is believed to contribute to heart issues, alongside lifestyle changes such as diet and marijuana use. |
| Delayed Medical Attention | 40% of Americans avoided seeking medical help during the pandemic, leading to potential gaps in care. |
| Potential Heart Conditions | Covid-19 has been associated with myocarditis and arrhythmias, impacting heart health. |
Summary
The increase in heart attacks among Americans is a grave concern as reports indicate a troubling rise in cardiac deaths occurring at home. Following the Covid-19 pandemic, there has been a striking 17 percent surge in heart-related fatalities, suggesting that many individuals are not receiving adequate medical attention. Factors such as changes in lifestyle, health-seeking behavior, and the direct impact of the pandemic on heart health are contributing to this alarming trend. Continued attention and action are necessary to address the decline in hospitalizations and ensure the safety of heart disease patients.